Efficient Neural Path Guiding with 4D Modeling
SessionPath Guiding, Scattering
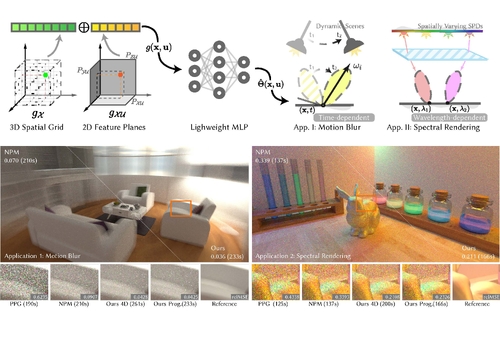
DescriptionPrevious local guiding methods used 3D data structures to model spatial radiance variations but struggled with additional dimensions in the path integral, such as temporal changes in dynamic scenes. Extending these structures to higher dimensions also proves inefficient due to the curse of dimensionality. In this study, we investigate the potential of compact neural representations to model additional scene dimensions efficiently, thereby enhancing the performance of path guiding in specialized rendering applications, such as distributed effects including motion blur. We present an approach that models a higher dimensional spatio-temporal distribution through neural feature decomposition. Additionally, we present a cost-effective approximate with lower-dimensional representation to model only subspace by progressive training strategy. We also investigate the benefits of modeling correlations with the additional dimensions on typical distributed ray tracing scenarios, including the motion blur effect in dynamic scenes, as well as spectral rendering. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on these applications.
Event Type
Technical Papers
TimeTuesday, 3 December 20244:53pm - 5:05pm JST
LocationHall B5 (2), B Block, Level 5






