GauWN: Gaussian-smoothed Winding Number and its Derivatives
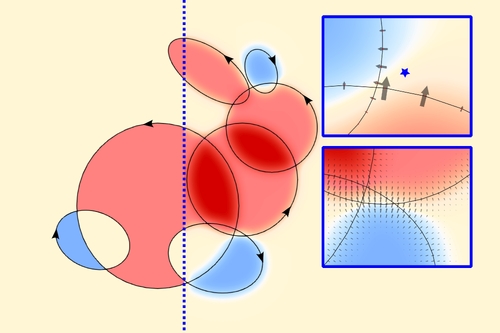
DescriptionFor a fixed polygon, one can easily determine whether a point is inside or
outside it using the winding number. However, deforming a given polygon
based on a set of points with expected inside/outside labeling is much more
difficult. It asks the winding number to be differentiable with respect to loca-
tions of the inside/outside test point and the polygon vertices. We propose a
method to address this even for a possibly intersected 2D polygon through
Gaussian kernel convolution. Our method can be applied to various prob-
lems such as resolving embedding issues (e.g., intersections), editing curves
using an in-out brush, and offsetting curves with feature preservation.
It may seem difficult to compute the value and derivatives of this smoothed
winding number (GauWN) efficiently, but the cost is only 4 to 6 times that of
the vanilla one. To achieve this efficiency, we employ two key strategies: 1)
For value computation, we extend the divergence theorem to handle self-
intersected cases and transform the convolution into a line integral that can
be computed efficiently. 2) For derivatives, we utilize local decomposition to
find a line integral form and leverage the radial symmetry and orthogonal
separability of the Gaussian kernel. With this differentiable winding number,
we can solve the aforementioned problems efficiently by formulating them
to involve both the explicit boundary and its implicit field. Surprisingly,
there is no need to create a background mesh despite the involvement of an
implicit field, making our method easy to apply.
outside it using the winding number. However, deforming a given polygon
based on a set of points with expected inside/outside labeling is much more
difficult. It asks the winding number to be differentiable with respect to loca-
tions of the inside/outside test point and the polygon vertices. We propose a
method to address this even for a possibly intersected 2D polygon through
Gaussian kernel convolution. Our method can be applied to various prob-
lems such as resolving embedding issues (e.g., intersections), editing curves
using an in-out brush, and offsetting curves with feature preservation.
It may seem difficult to compute the value and derivatives of this smoothed
winding number (GauWN) efficiently, but the cost is only 4 to 6 times that of
the vanilla one. To achieve this efficiency, we employ two key strategies: 1)
For value computation, we extend the divergence theorem to handle self-
intersected cases and transform the convolution into a line integral that can
be computed efficiently. 2) For derivatives, we utilize local decomposition to
find a line integral form and leverage the radial symmetry and orthogonal
separability of the Gaussian kernel. With this differentiable winding number,
we can solve the aforementioned problems efficiently by formulating them
to involve both the explicit boundary and its implicit field. Surprisingly,
there is no need to create a background mesh despite the involvement of an
implicit field, making our method easy to apply.
Event Type
Technical Papers
TimeTuesday, 3 December 20249:00am - 12:00pm JST
LocationHall C, C Block, Level 4







